4 minutes
Do not use Pandas to load data use Data Factory
I recently wrote blog post about how to connect pandas to your SQL database and read file from SQL server.
pandas is a fantastic tool to analyse and manipulate data. I use it all the time. It is very efficient if the “size” of the data is say up to 1 million records and can be done in your local machine or in a VM fairly quick calculations. No problems at all.
With the data connection created with SQL Server it works both ways. The same way you can read data from SQL Server but also can write to it. This is where is the problem with pandas. Because you can it does not mean you SHOULD do it.
Reason it is very slow compared to other options.
How slow?
Let’s test and then compare to a proper ETL tool for data ingestion like Azure Data Factory
To do this test I will user the NYC Taxi dataset with the 2016 data I got from Kaggle
So here is the script to upload from my local machine using a broadband connection straight from csv to pandas then to SQL.
import os
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
import pandas as pd
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from utils import timing
SQL_SERVER = os.getenv('SQL_SERVER')
SQL_DATABASE = os.getenv('SQL_DATABASE')
SQL_USER_NAME = os.getenv('SQL_AZURE_USERNAME')
SQL_PASSWORD = os.getenv('SQL_AZURE_PASSWORD')
driver= '{ODBC Driver 18 for SQL Server}'
@timing
def run_script():
odbc_params = f'DRIVER={driver};SERVER=tcp:{SQL_SERVER};PORT=1433;DATABASE={SQL_DATABASE};UID={SQL_USER_NAME};PWD={SQL_PASSWORD}'
connection_string = f'mssql+pyodbc:///?odbc_connect={odbc_params}'
engine = create_engine(connection_string)
taxi = pd.read_csv('taxi.csv')
taxi[:1000].to_sql("taxi",con=engine, if_exists="replace", index=False)
engine.dispose()
run_script()
# func: run_script took: 39.0262 sec
Lets only upload 1000 rows and estimate the total time otherwise it is going to take a LOT of time and I don’t have that much to waste.
So I have a decorator to time the execution of the function and the run took.
~39 seconds
so to extrapolate to 1,458,644 rows that would take ~15.8 hours to load it all. So not acceptable.
How long it would take it using ADF (Azure Data Factory)?
So to make things easy lets use python to upload it to a data lake storage and then from there to SQL DB using ADF.
Here is a script to upload to blob storage from local
import configparser
import io
import pandas as pd
from azure.storage.blob import BlobServiceClient
from utils import timing
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read('config.ini')
PEDRO_LAKE_STORAGE_KEY = config.get('STORAGE', 'key')
PEDRO_LAKE_STORAGE_STRING = config.get('STORAGE','string')
folder = 'landing/large-data'
def upload_to_blob(df: pd.DataFrame, container:str, blob_name:str)-> None:
buffer = io.BytesIO()
df.to_csv(buffer, index=False)
buffer.seek(0)
blob_service_client = BlobServiceClient.from_connection_string(conn_str=PEDRO_LAKE_STORAGE_STRING)
container_client = blob_service_client.get_container_client(container)
container_client.upload_blob(name=blob_name, data=buffer, overwrite=True)
@timing
def run_script():
taxi = pd.read_csv('taxi.csv')
upload_to_blob(taxi, folder, 'taxi.csv')
run_script()
# func: run_script took: 104.326 sec
So now it was not too bad. It took only only 104 seconds to load all text data. Now I understand why ELT not ETL is so efficient.
The data has no schema, but it was 550x faster.
Now from ADF Blob to SQL.
So it took 5 minutes.
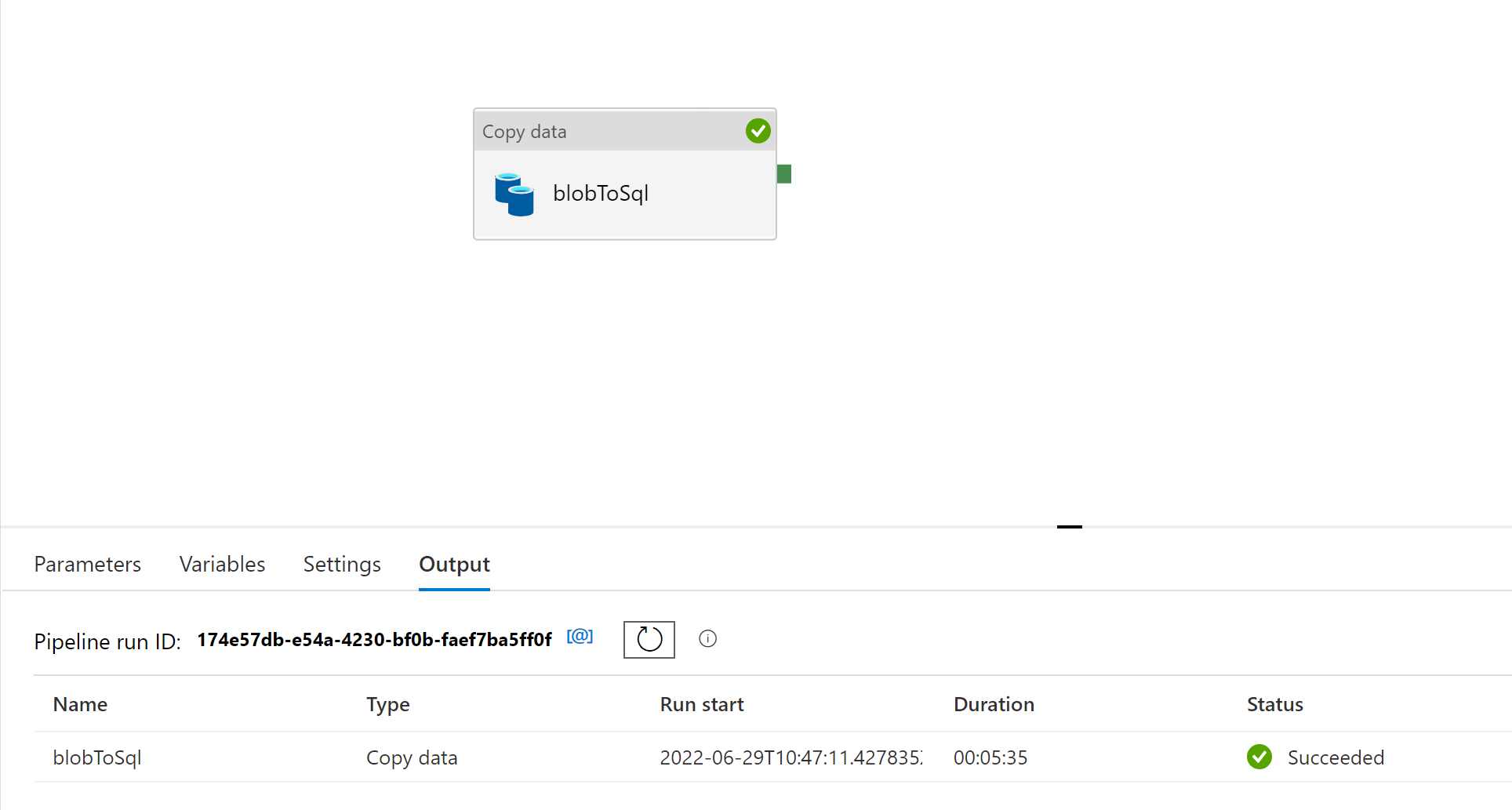
ADF
this is ~186x faster and the data is in a database with structure and schema. Added index this is very efficient do do queries. Specially if in servers like MPP (Massive parallel processing)
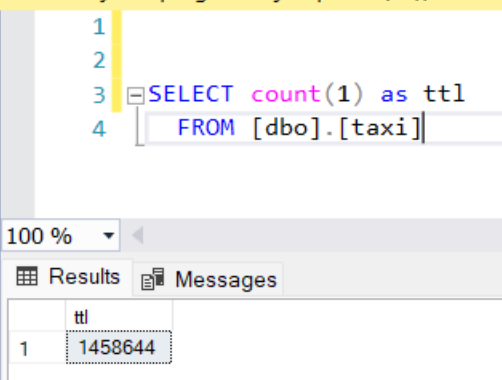
SSMS
So to try another thing I will load the same data as a parquet format which is compressed and then load to SQL and time it.
For this I am using pyarrow which is a python wrapper for the c++ library Apache Arrow. It is REALLY fast. It is worth another post for that one.
here is a script to read the csv and load it to the blob storage.
import configparser
import adlfs
from pyarrow import csv
import pyarrow.parquet as pq
import pyarrow.compute as pc
from utils import timing
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read('config.ini')
AZURE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT_KEY = config.get('STORAGE', 'key')
AZURE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT_STRING = config.get('STORAGE','string')
AZURE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME = config.get('STORAGE','AZURE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME')
AZURE_STORAGE_CONTAINER_NAME = "landing/large-data"
@timing
def run_script():
fs = adlfs.AzureBlobFileSystem(account_name=AZURE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME, account_key=AZURE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT_STRING,
connection_string=AZURE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT_STRING)
taxi = csv.read_csv("taxi.csv")
pq.write_table(taxi, f"{AZURE_STORAGE_CONTAINER_NAME}/taxi.parquet" , filesystem=fs)
run_script()
# func: run_script took: 14.893 sec
this one took 15 seconds.
csv is 186 Mb parquet same data is 43 Mb (23% of csv size)
So load csv, transform in parquet and load to blog it took only 14% of the time that pandas took to load the csv.
Finally the LAST test.
from parquet to (blob) to SQL server using ADF.
it took slightly less than the csv. like 4.8 minutes. So this one I expected better. But it is what it is. I just did one run each.
Here is a chart with the summary
Also here is the script for the decorator to time the function
#utils.py
from functools import wraps
from time import time
def timing(f):
@wraps(f)
def wrap(*args, **kw):
ts = time()
result = f(*args, **kw)
te = time()
print(f'func: {f.__name__} took: {te-ts:2.4f} sec')
return result
return wrap